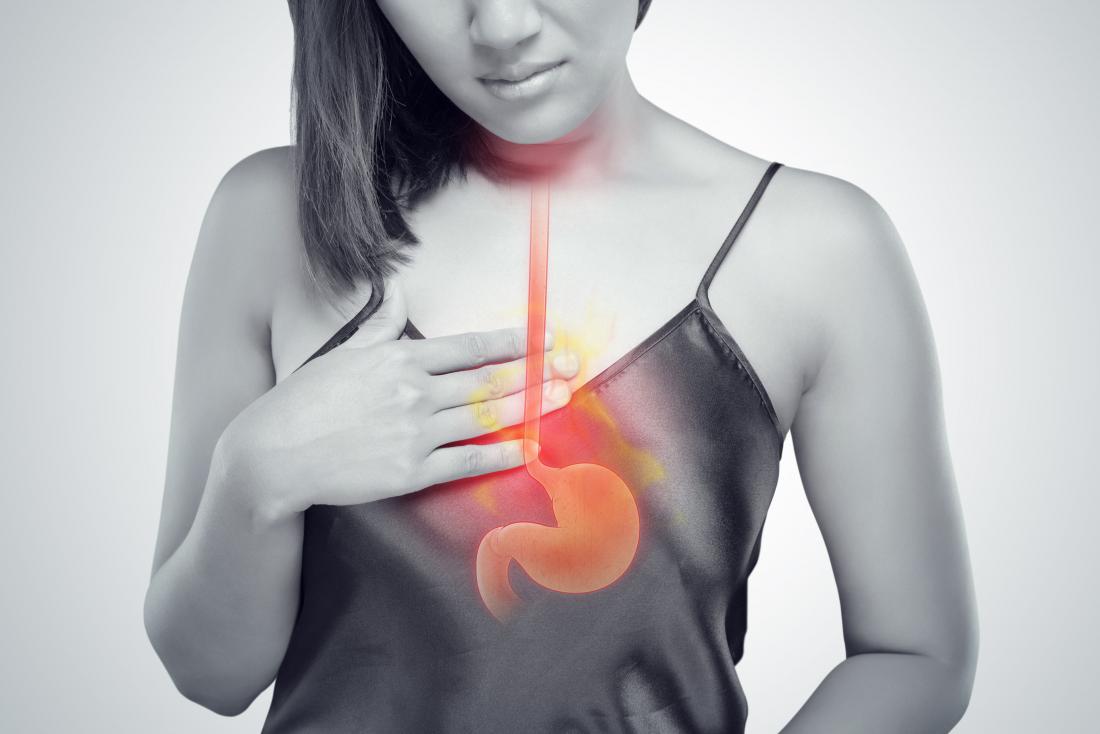
Understanding Acid Reflux: Symptoms and Remedies

Key Highlights
- Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD is a common condition affects about 20% of people in the United.
- Symptoms of acid reflux include heartburn, regitation of food or liquid, cough, hoarseness, and chest pain.
- Lifestyle changes such as weight loss, avoiding trigger foods, and not lying down after meals can help alleviate symptoms.
- Home remedies like herbal teas and aloe vera can provide relief from acid reflux.
- Medical treatments for acid reflux include over-the-counter antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and prescription medications.
Introduction
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. While occasional acid reflux is normal and can be managed with simple lifestyle changes, frequent or persistent acid reflux can be a sign of GERD and may require medical treatment.
In this blog, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and remedies for acid reflux. We will explore the science behind acid reflux, the difference between acid reflux and GERD, and how to identify the symptoms of acid reflux in adults and children. We will also delve into the causes and risk factors of acid reflux, including dietary and lifestyle influences. Additionally, we will provide preventive measures and lifestyle modifications that can help alleviate acid reflux symptoms. Finally, we will discuss home remedies and medical treatments for acid reflux, as well as the potential complications of untreated acid reflux.
Understanding acid reflux is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. By implementing lifestyle changes, exploring home remedies, and seeking medical treatment when necessary, individuals can find relief from acid reflux and prevent complications associated with the condition.
What is Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux, occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This happens due to a malfunctioning valve called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which is located at the junction of the esophagus and the stomach. Normally, the LES closes after food passes through it, preventing stomach acid from entering the esophagus. However, when the LES doesn’t close properly or opens too frequently, acid reflux can occur.
The stomach contains hydrochloric acid, a strong acid that helps break down food. When this acid flows back into the esophagus, it can cause irritation and inflammation, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. The esophagus is not designed to handle the corrosive effects of stomach acid, unlike the stomach lining, which is protected by a layer of mucus.
In some cases, acid reflux can progress to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a more severe form of acid reflux. GERD is typically diagnosed when acid reflux symptoms occur more than twice a week and interfere with daily life. It is important to seek medical attention and provide your medical history if acid reflux symptoms persist or worsen, as untreated GERD can lead to complications such as esophageal strictures and Barrett’s esophagus.
The Science Behind Acid Reflux
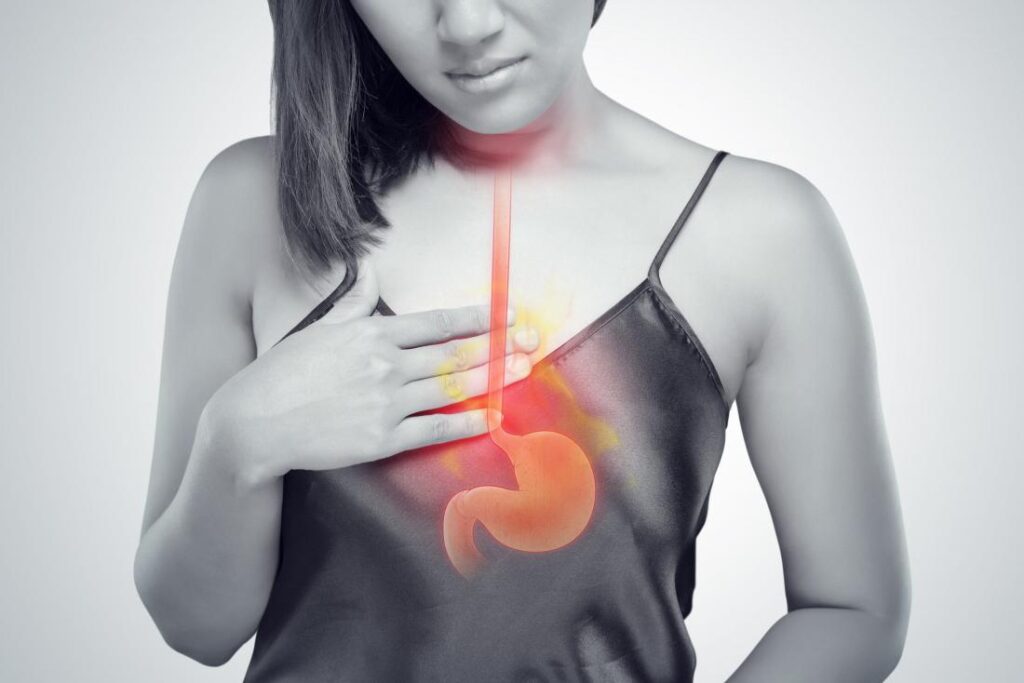
Acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle at the end of the esophagus, fails to close properly or opens too frequently. This allows stomach acid and partially digested food to flow back into the esophagus. The LES is responsible for preventing the backflow of stomach contents and maintaining the separation between the stomach and the lower esophagus.
When the LES doesn’t function properly, the acidic gastric contents can irritate the lining of the esophagus, leading to the symptoms commonly associated with acid reflux. These symptoms may include heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest or throat, regurgitation of food or liquid, and a sour or bitter taste in the mouth.
The acidity of the stomach contents, particularly the hydrochloric acid, can cause inflammation and damage to the delicate lining of the esophagus. Over time, this can lead to complications such as esophageal strictures, narrowing of the esophagus, and Barrett’s esophagus, a precancerous condition.
Understanding the science behind acid reflux is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. Lifestyle modifications, home remedies, and medical treatments can all play a role in alleviating acid reflux and improving quality of life.
Distinguishing Between Acid Reflux and GERD
While acid reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are related, there is a distinction between the two conditions. Acid reflux refers to the occasional backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. It can also cause nausea, making it important to distinguish between acid reflux and other conditions. It is a common occurrence and can be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter antacids.
On the other hand, GERD is a chronic condition characterized by frequent acid reflux episodes, occurring more than twice a week. The symptoms of GERD can be more severe and persistent, often interfering with daily activities. In addition to the typical symptoms of acid reflux, individuals with GERD may experience difficulty swallowing, chronic cough, hoarse voice, and weight loss.
It is important to distinguish between acid reflux and GERD as the treatment approaches may differ. While occasional acid reflux can often be managed with lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter medications, GERD may require prescription medications or surgical interventions to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Identifying Symptoms of Acid Reflux
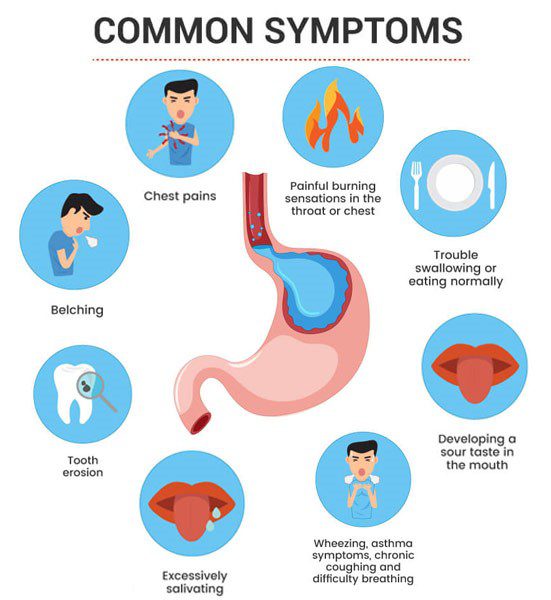
Identifying the symptoms of acid reflux is essential for understanding and managing the condition. The primary symptom of acid reflux is heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest or throat. Other common symptoms include regurgitation of food or liquid, where the stomach contents flow back into the mouth, a persistent sore throat, and a burning feeling in the chest or throat.
It is important to note that the symptoms of acid reflux can vary among individuals, and some people may experience atypical symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty swallowing, chronic cough, or hoarseness. Recognizing these symptoms can help individuals seek appropriate medical attention and implement lifestyle changes or treatments to alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
Common Symptoms in Adults
In adults, the most common symptom of acid reflux is heartburn. This is often described as a burning sensation in the chest that can radiate up to the neck and throat. It is typically triggered by eating certain foods or lying down after a meal. Other symptoms of acid reflux in adults may include regurgitation of food or liquid, which can happen when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) does not close properly, allowing stomach contents to flow back up into the esophagus. This can cause a sour or bitter taste in the mouth. If you experience these symptoms on a regular basis, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Recognizing Symptoms in Children
Acid reflux can also occur in children, and it’s important to recognize the symptoms. Persistent acid reflux in children may present as frequent spitting up or vomiting. They may have trouble swallowing or experience gagging or choking. Children with acid reflux may also have wet burps or hiccups, and they may be irritable or arch their back during or after feeding. In some cases, children may develop a recurring cough, chest pain, or complain of a sore throat. If you notice these symptoms in your child, it’s important to consult their pediatrician for an evaluation and proper treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of acid reflux. One common cause is eating large meals or lying down immediately after eating, as this can put pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and cause stomach contents to flow back up into the esophagus. Another factor is a hiatal hernia, which occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. This can weaken the LES and lead to acid reflux. Obesity is also a risk factor, as excess weight can put pressure on the abdomen and increase the likelihood of stomach acid flowing back up into the esophagus. Other factors that can contribute to acid reflux include smoking, certain medications, and certain medical conditions.
Dietary Influences on Acid Reflux

Diet plays a significant role in the development and management of acid reflux. Certain foods and beverages can trigger symptoms by increasing the production of stomach acid or weakening the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Some common dietary influences on acid reflux include consuming large meals, particularly high in fat, as this can delay stomach emptying and increase the risk of acid reflux. Other triggers may include spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, onions, garlic, chocolate, caffeine, and carbonated beverages. Consulting with a gastroenterologist, such as Ekta Gupta, M.B.B.S., M.D., can help identify these trigger foods and provide personalized dietary recommendations to manage and reduce symptoms of acid reflux. Making dietary changes, such as opting for smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding trigger foods, can greatly improve symptoms and provide relief.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors

In addition to dietary influences, certain lifestyle and environmental factors can contribute to the development and worsening of acid reflux. Smoking is a significant risk factor, as it can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and lead to acid reflux. Making simple lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and managing stress through relaxation techniques can greatly improve symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Other environmental factors, such as exposure to secondhand smoke and hormonal changes during pregnancy, specifically the hormone progesterone, can also contribute to acid reflux. It’s important to identify and address these lifestyle and environmental factors to effectively manage and reduce acid reflux symptoms.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing acid reflux involves making certain lifestyle modifications and adopting healthy habits. Maintaining a healthy weight is important, as excess weight can put pressure on the abdomen and contribute to acid reflux. Making simple lifestyle changes such as avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller, more frequent meals, and avoiding lying down immediately after eating can also help prevent symptoms. Elevating the head of the bed by using pillows or raising the mattress can reduce the likelihood of stomach acid flowing back up into the esophagus during sleep. By implementing these preventive measures and lifestyle modifications, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing acid reflux and manage symptoms effectively.
Dietary Changes to Alleviate Symptoms
Dietary changes can play a crucial role in alleviating the symptoms of acid reflux. Avoiding trigger foods such as spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, onions, garlic, chocolate, caffeine, and carbonated beverages can help reduce the production of stomach acid and prevent acid reflux symptoms. Opting for smaller, more frequent meals can also help prevent excessive stomach acid production and promote better digestion. It’s important to eat slowly and chew food thoroughly to aid digestion and reduce the risk of acid reflux. Additionally, incorporating foods that have a soothing effect on the stomach, such as ginger, oatmeal, and yogurt, can help alleviate symptoms and promote better digestive health.
Importance of Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in managing and preventing acid reflux. Obesity is a significant risk factor for acid reflux, as excess weight can put pressure on the abdomen and increase the likelihood of stomach acid flowing back up into the esophagus. Losing weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce symptoms and prevent the development of acid reflux. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can alleviate the pressure on the abdomen, promote better digestion, and reduce the risk of complications associated with acid reflux.
Home Remedies for Acid Reflux
In addition to lifestyle and dietary changes, there are several home remedies that can provide relief from acid reflux symptoms. Herbal teas, such as chamomile or ginger tea, can help soothe the stomach and reduce inflammation. Aloe vera juice or gel can also provide relief by calming the digestive system and reducing irritation. Other home remedies include chewing gum to increase saliva production, which can help neutralize stomach acid, and avoiding tight-fitting clothing that puts pressure on the abdomen. These simple home remedies can be effective in managing and reducing the symptoms of acid reflux.
Herbal Teas and Their Benefits
Herbal teas have long been used as natural remedies for various ailments, including acid reflux. Certain herbal teas can provide relief by soothing the stomach and promoting better digestion. Some herbal teas that are beneficial for acid reflux include chamomile tea, which has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce irritation and inflammation in the esophagus. Ginger tea can help calm the digestive system and reduce symptoms of acid reflux. Peppermint tea, on the other hand, should be avoided, as it can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and worsen acid reflux symptoms. By incorporating these herbal teas into your daily routine, you can help alleviate symptoms and promote better digestive health.
The Role of Aloe Vera and Ginger
Aloe vera and ginger are two natural remedies that can provide relief from acid reflux symptoms. Aloe vera has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an effective remedy for reducing irritation and inflammation in the esophagus. It can be consumed as a juice or gel. Ginger, on the other hand, can help calm the digestive system and reduce symptoms of acid reflux. It has anti-inflammatory properties and can help promote better digestion. Incorporating aloe vera and ginger into your diet or consuming them in the form of teas or supplements can provide relief and support better digestive health.
Medical Treatments for Acid Reflux
In addition to lifestyle changes and home remedies, there are medical treatments available for acid reflux. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly prescribed medications that reduce the production of stomach acid, providing relief from acid reflux symptoms. Antacids can also be used to neutralize stomach acid and provide temporary relief. These over-the-counter medications are available in various forms, such as tablets, liquids, and chewable tablets. In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary to manage severe or persistent acid reflux symptoms. These medications may include H2 blockers, which reduce stomach acid production, or prokinetic agents, which help improve the movement of food through the digestive system. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate medical treatment for your specific condition.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Over-the-counter solutions can provide temporary relief from acid reflux symptoms. Antacids, such as Tums or Rolaids, can help neutralize stomach acid and provide quick relief from heartburn. They are available in various forms, such as chewable tablets or liquids, and can be taken as needed. However, it’s important to note that antacids only provide temporary relief and do not address the underlying cause of acid reflux. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
When to Consider Prescription Medications
In some cases, over-the-counter solutions may not be sufficient to manage severe or persistent acid reflux symptoms. If symptoms are not adequately controlled with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications, it may be necessary to consider prescription medications. Prescription proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole or esomeprazole, are commonly prescribed to reduce stomach acid production and provide long-term relief from acid reflux symptoms. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional when using prescription medications for acid reflux, as they may have potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure the safe and effective use of prescription medications for acid reflux.
Understanding Complications of Untreated Acid Reflux
If left untreated, acid reflux can lead to complications that can significantly impact your health. One of the potential complications is an esophageal stricture, which is a narrowing of the esophagus due to the formation of scar tissue. This can make it difficult for food and liquids to pass through the esophagus, leading to difficulty swallowing and discomfort. Another complication is Barrett’s esophagus, which is a condition characterized by changes in the lining of the esophagus. It is considered a precancerous condition and increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer. Regular monitoring and management of acid reflux symptoms are important to prevent these complications. Seeking medical treatment and making necessary lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of complications and ensure proper management of acid reflux.
Potential Risks of Long-Term GERD
Long-term gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can have serious implications for your health. Chronic exposure to stomach acid can cause inflammation and damage to the lining of the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. Over time, this chronic inflammation can result in the development of esophageal ulcers, bleeding, and strictures, which can significantly impact your quality of life. In some cases, long-term GERD can also increase the risk of developing Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer. It’s crucial to seek medical treatment and management of GERD symptoms to prevent these serious complications. Making lifestyle changes, taking prescribed medications, and regularly monitoring your condition are essential for long-term management of GERD.
Link Between Acid Reflux and Esophageal Cancer
There is a link between acid reflux and the development of esophageal cancer. Chronic exposure to stomach acid can cause inflammation and damage to the lining of the esophagus, increasing the risk of developing Barrett’s esophagus. Barrett’s esophagus is a precancerous condition that can progress to esophageal cancer if left untreated. Other risk factors for esophageal cancer include smoking, obesity, and a family history of the disease. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience frequent or persistent acid reflux symptoms to prevent the development of complications such as Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer. Regular monitoring and management of acid reflux symptoms are essential for early detection and treatment of any potential precancerous or cancerous changes in the esophagus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding acid reflux symptoms and remedies is crucial for managing this condition effectively. By recognizing the signs, causes, and risk factors, you can make informed lifestyle changes to alleviate symptoms. Incorporating preventive measures like dietary adjustments, weight management, and home remedies can also offer relief. For more severe cases, medical treatments ranging from over-the-counter solutions to prescription medications may be necessary. It’s essential to address acid reflux promptly to prevent complications such as GERD and potential risks like esophageal cancer. Stay informed, follow a balanced approach, and consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing acid reflux effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Acid Reflux Go Away on Its Own?
Acid reflux symptoms can improve and even go away with self-management and lifestyle changes. These may include weight loss, avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining good dietary habits. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.
How Often Should Someone with Acid Reflux Eat?
Individuals with acid reflux should consider eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This can help prevent excessive stomach acid production and reduce the risk of acid reflux symptoms. Waiting 2-3 hours after eating before lying down can also aid in digestion and prevent stomach contents from flowing back up into the esophagus.
Are There Any Permanent Cures for Acid Reflux?
While there is no permanent cure for acid reflux, it can be effectively managed and controlled through medical treatment and lifestyle modifications. Regular monitoring, adherence to prescribed medications, and making necessary dietary and lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications associated with acid reflux.
How Does Stress Affect Acid Reflux?
Stress can exacerbate acid reflux symptoms by increasing the production of stomach acid and weakening the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Managing stress through relaxation techniques and making lifestyle changes can help reduce the impact of stress on acid reflux and alleviate symptoms.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4562453
https://links.e.response.mayoclinic.org/EmailPreview-GI
https://apm.amegroups.com/article/view/38240/29295
https://www.health.harvard.edu/newsletter_article/proton-pump-inhibitors
https://www.nuritionletter.tufts.edu/gi-health/handling-your-heartburn